
Citation: Kaur S. A Descriptive Study to Assess the Knowledge of Labour Workers Regarding Personal Protective Equipments in Baru Sahib, Distt Sirmour, Himachal Pradesh. Nurs Health Care Int J 2017, 1(5): 000129.
*Corresponding author: Simarjeet Kaur, Department of Community Health Nursing, Eternal University, India, Tel: 8427016084; Email: simarjeet3011@gmail.com
Introduction:Occupational health deals with all aspects of health and safety in the workplace and has a strong focus on primary prevention of hazards. Personal protective equipment can help protect against many of health hazards. Knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipment is one of the key factors to maintain the health and safety of workers.
Aim of Study: The aim of study was to assess the knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments in Baru Sahib, Distt Sirmour, Himachal Pradesh.
Material and Methods: Study was conducted in Baru Sahib, Distt Sirmour, Himachal Pradesh. Quantitative research approach and descriptive research design was used to assess the knowledge regarding personal protective equipments and purposive sampling technique was used to select 60 labour workers of Baru Sahib. Structured interview schedule was prepared to assess the knowledge regarding personal protective equipments.
Results: The findings of study revealed that majority of labour workers 33(55%) had average knowledge, 20(33.33%) labour workers had good knowledge and below average knowledge was possessed by 7(11.67%) labour workers of Baru Sahib. In present study educational status, family per capita monthly income, type of work and nearby health facility had significant impact on knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments.
Conclusion: It was concluded on the basis of the findings of study that labour worker has average knowledge regarding personal protective equipments.
Keywords: Knowledge; Labour worker; Personal protective equipments
“Obedience is the mother of success and is wedded to safety”- Aeschylus
Work plays a central role in people’s lives since most workers spend at least 8 hours a day in the work place whether it is on a construction site, in an office or factory [1]. According to ILO/WHO committee on occupational health “occupational health should aim at the promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social wellbeing of worker in all occupation; the prevention among workers of departures from health caused by their working condition; the protection of worker in their employment from risks resulting from factors adverse health; the placing and maintenance of the worker in an occupational environment adapted to his physiological and psychological equipment and summarize the adaption of work to man and of each man to his job”[2].
Labour workers suffer from more serious injuries and fatalities than the general workforce population. They die from work-related trauma at a rate three times the average for workers in all industrial sectors; they suffer disproportionately from non-fatal injuries, from lung diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, hearing loss and dermatologic conditions [3].
According to recent published report by Compensation Act, 33.63% fatal accident are recorded and 49.11% related to permanent disablement of people working as labour worker 17.26% were temporary disablement cases are recorded in India [4].
Personal protective equipments are devices that will protect the user against health or safety risks at work. It can include item such as safety helmets, gloves, eye protection, high visibility clothing, safety foot wear, it also include respiratory protective equipment. Health injuries and illnesses may result from contact with chemical, radiological, physical, electrical, mechanical or other work place hazards [5].
Objectives-To assess the knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments.
-To find out the association of knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments with selected demographic variables
Assumptions-Labour workers will have some knowledge regarding personal protective equipments.
-Labour workers may have health problems related to occupation.
Materials and MethodsThe present study was carried out in Baru Sahib, Distt. Sirmour, Himachal Pradesh. A quantitative research approach and Non experimental descriptive research design was used. Total sample of study was 60 labour workers (15-53 years) selected through purposive sampling technique. In view of the nature of the problem and to accomplish the objectives of the study, structured interview was used. Validity was ensured in consultation with guides and experts in the field of nursing. Reliability of the structured interview schedule was tested by using split half formula (r = 0.81). After obtaining formal permission from concerned authority structured interview schedule was used to collect the needed data. Both descriptive and inferential statistics was used to analyse the data.
Results- Distribution of labour workers according to age revealed that most of the labour workers 23(38.33%) were in age group of 24-33 years and Only 2(3.34%) were in age group 44-53 years respectively.
-Majority of labour workers 46(76.66%) were Hindu and 4(6.67%) were Sikh respectively. Most of the labour workers 21(35%) were illiterate and 3(5%) were educated up to senior secondary school education respectively. Majority of labour workers 31(51.67%) were unmarried followed by 29(48.33%) were married. -Distribution of labour workers according to family per capita revealed that most of the labour workers 21(35%) were having income per capita 1671-2785 and 5(8.33%) were having 2786-5570respectively.
-In relation to type of work, majority of the labour workers 39 (65%) were engaged in construction, followed by 11(18.33%) were engaged in other works like electrician, 6(10%) were engaged in carpentry and 4(6.67%) were engaged in welding respectively.
-Distribution of labour workers according to working hour per day revealed that majority of labour workers 45(75%) were working for less than 9 hours and 1 (1.67%) working for more than 12 hours respectively. Most of the labour workers 24(40%) were having more than 5 years’ experience and 9(15%) were having less than 1 year respectively.
-Majority of labour workers 33(55%).
prefers Charitable hospital, followed by 23(38.33%) prefers PHC, 3(5%) prefers other health facility like sub centre and 1 (1.66%) prefers specialist hospitals respectively.
Objective: 1- To assess the knowledge score of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments.
Table 1, Figure 1 Shows Frequency and Percentage distribution of labour workers in terms of level of knowledge. The data revealed that majority of labour workers 33(55%) had average knowledge, 20(33.33%) labour workers had good knowledge and below average knowledge was possessed by 7(11.67%) labour workers of Baru sahib.
Objective: 2 To find out the association of knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments with selected demographic variables
-The data revealed that educational status, family per capita monthly income, type of work, nearby health facility has significant association with knowledge score of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments as the calculated p value is less than .05. Hence they were statistically significant at the level p<0.05.
DiscussionThe present study “A descriptive study to assess the knowledge of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments in Baru Sahib, Distt Sirmour, Himachal Pradesh revealed that majority of labour workers 33(55%) had average knowledge, 20(33.33%) labour workers had good knowledge and below average knowledge was possessed by 7(11.67%) labour workers of Baru sahib and educational status, family per capita monthly income, type of work, nearby health facility has significant association with knowledge score of labour workers regarding personal protective equipments as p<0.05. The above findings were consistent with the study conducted by Truong Cong dat (2015) [6] who reported the majority of labour workers (78.2%) had average knowledge regarding personal protective equipments and it reported that educational status had significant impact on knowledge of labour workers.
Nursing Implications-Training programmed should be planned by occupational nurses in whom trainers will teach about benefits of using personal protective equipments and occupational hazards for promoting the health of labour workers.
-The nurse should educate labour workers who are utilizing personal protective equipments about the importance and right of using them at construction site as provided under labour act.
Nursing Education-The community health nursing and medical surgical nursing curriculum for all levels of nursing should give emphasis on utilization personal protective equipments for labour workers and its benefits based on finding of this study.
-Many conference, workshops, seminars can be conducted in nursing colleges at national and international level regarding knowledge utilization personal protective equipments of labour workers.
Nursing Administration-The nurse administrator should develop Education and awareness programme related to the recent changes in the aspects of personal protective equipments which will enable the nurses to update their knowledge, acquire special skills and demonstrate high quality care for the prevention and cure of occupational hazards to the labour workers.
Community Health NursingPublic education, media campaigns by students in addition to the available health care facilities will result in significant increase in knowledge about personal protective equipments.
RecommendationsOn the basis of the findings following recommendations have been made for further study:
-A quantitative study can be conducted to assess attitude and utilization of personal protective equipments among labour workers.
A qualitative study can be conducted on the prevalence, attitude of labour workers regarding occupational hazards due to inadequate use of personal protective equipments.
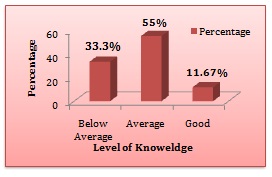
Figure 1: Bar diagram showing percentage distribution of labour workers in terms of levels of knowledge regarding personal protective equipments.
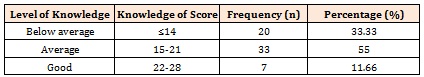
Table 1: Frequency and Percentage Distribution of labour workers in terms of knowledge score regarding personal protective equipments
Chat with us on WhatsApp